Step into the world of the Federal Reserve where financial magic meets economic stability. Get ready for a rollercoaster ride through the intricate workings of this powerful institution.
As we delve deeper, you’ll uncover the secrets behind the Federal Reserve’s structure, history, monetary policy, financial stability role, and much more.
What is the Federal Reserve?
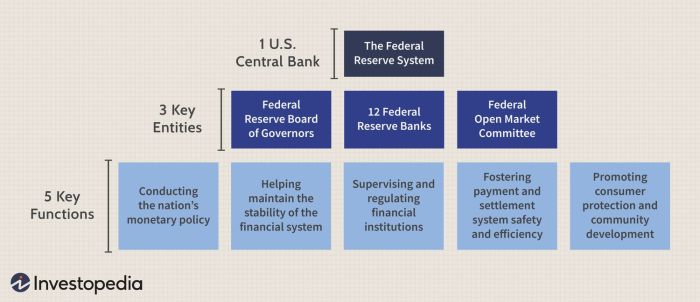
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the Fed, is the central bank of the United States. It plays a crucial role in the country’s financial system by regulating monetary policy, supervising and regulating banks, and maintaining the stability of the financial system.
Role and Purpose of the Federal Reserve
The primary role of the Federal Reserve is to control the nation’s money supply and interest rates to achieve economic stability. It aims to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates. Additionally, the Fed acts as a lender of last resort to provide liquidity to banks during financial crises.
- Conducting monetary policy through open market operations, setting reserve requirements, and adjusting the discount rate.
- Supervising and regulating financial institutions to ensure the safety and soundness of the banking system.
- Maintaining financial stability by monitoring and addressing risks in the financial system.
Structure of the Federal Reserve System
The Federal Reserve System is composed of three main components: the Board of Governors, the Federal Reserve Banks, and the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).
- The Board of Governors, located in Washington, D.C., sets the monetary policy and provides oversight to the Federal Reserve Banks.
- There are 12 Federal Reserve Banks located throughout the country, each responsible for supervising and regulating banks within its district.
- The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is responsible for setting the target federal funds rate and implementing monetary policy decisions.
Functions performed by the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve performs various functions to fulfill its mandate of promoting economic stability and growth.
- Issuing currency and regulating its circulation to ensure the integrity of the currency system.
- Acting as a fiscal agent for the U.S. government by processing payments, issuing government securities, and managing the Treasury’s cash balances.
- Supervising and regulating financial institutions to maintain the safety and soundness of the banking system.
History of the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the Fed, was established on December 23, 1913, with the signing of the Federal Reserve Act by President Woodrow Wilson. This was in response to the financial panics that occurred in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, highlighting the need for a central banking system in the United States.
Establishment of the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve was created to provide the country with a safer, more flexible, and more stable monetary and financial system. It consists of the Board of Governors, 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks, and the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). The Fed’s main objectives are to conduct monetary policy, supervise and regulate financial institutions, and maintain the stability of the financial system.
Key Events in the History of the Federal Reserve
- The Great Depression: During the 1930s, the Federal Reserve implemented various policies to counter the effects of the Great Depression, such as lowering interest rates and increasing the money supply.
- Bretton Woods Agreement: In 1944, the Bretton Woods Agreement established a system of fixed exchange rates, with the U.S. dollar pegged to gold, which influenced the Fed’s monetary policy.
- The Financial Crisis of 2007-2008: The Federal Reserve played a key role in responding to the financial crisis by implementing unconventional monetary policies like quantitative easing to stabilize the economy.
Comparison of Functions in the Past and Present
| Functions | Past | Present |
|---|---|---|
| Monetary Policy | Primarily focused on controlling inflation and interest rates. | Expanded to include managing economic growth and employment. |
| Regulation | Focused on supervising banks and ensuring financial stability. | Regulatory responsibilities have increased to prevent future financial crises. |
| Financial Stability | Emphasized stability of the banking system. | Now includes monitoring systemic risks and promoting overall financial stability. |
Monetary Policy
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by the Federal Reserve to manage the supply of money in the economy in order to achieve specific goals such as controlling inflation, stabilizing prices, and promoting economic growth.
Implementing Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve implements monetary policy through three main tools:
- Open Market Operations: The buying and selling of government securities to control the money supply in the economy.
- Discount Rate: The interest rate at which banks can borrow money directly from the Federal Reserve.
- Reserve Requirements: The amount of funds that banks are required to hold in reserve to ensure stability and liquidity.
Impact of Monetary Policy
Monetary policy has a direct impact on inflation and interest rates in the economy. When the Federal Reserve tightens monetary policy by decreasing the money supply, it can help reduce inflation but may lead to higher interest rates. Conversely, when the Fed loosens monetary policy by increasing the money supply, it can stimulate economic growth but may result in higher inflation rates.
Role in Financial Stability
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in maintaining financial stability in the United States. By overseeing the banking system and implementing monetary policy, the Fed works to prevent financial crises and ensure the overall health of the economy.
Intervention During Financial Crises
During times of financial turmoil, the Federal Reserve intervenes by providing liquidity to the markets. This can involve lowering interest rates, purchasing government securities, or implementing emergency lending programs to stabilize the financial system. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, the Fed took unprecedented actions to prevent a complete collapse of the banking sector.
Relationship with the Banking System
The Federal Reserve closely monitors and regulates banks to ensure they are operating safely and soundly. Through its supervision and regulation functions, the Fed aims to prevent bank failures and maintain the stability of the financial system. By setting reserve requirements and conducting stress tests, the Fed helps to strengthen the banking system and protect against systemic risks.
Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are crucial aspects of any central bank’s operations, including the Federal Reserve. The level of transparency in decision-making processes and the mechanisms in place for ensuring accountability are essential for maintaining public trust and confidence in the institution.
Transparency of Decision-Making
The Federal Reserve aims to be transparent in its decision-making processes to provide clarity to the public and market participants. One way it achieves this is through the publication of meeting minutes, economic projections, and statements following policy meetings. Additionally, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) releases statements explaining the rationale behind interest rate decisions, providing insight into the factors influencing monetary policy.
- The release of meeting minutes allows the public to understand the discussions and considerations that led to policy decisions.
- Economic projections provide forecasts on key economic indicators, giving insight into the Fed’s outlook on the economy.
- Statements following policy meetings Artikel the decision and the reasoning behind it, promoting transparency in communication.
Accountability Mechanisms
To ensure accountability, the Federal Reserve is subject to oversight by Congress and undergoes regular audits by the Government Accountability Office (GAO). The Fed Chair testifies before Congress, providing an opportunity for lawmakers to question and hold the institution accountable for its actions. Additionally, the FOMC’s decisions are subject to review and scrutiny, contributing to a system of checks and balances.
- Congressional oversight and audits by the GAO help ensure that the Federal Reserve operates in the best interest of the public.
- Testimonies by the Fed Chair provide a platform for accountability and transparency in decision-making processes.
- Review and scrutiny of FOMC decisions contribute to the Fed’s accountability to the public and financial markets.
Comparison to Global Central Banks
Compared to other central banks globally, the Federal Reserve is often seen as more transparent in its communication and decision-making processes. Many central banks around the world follow the Fed’s lead in providing more information to the public and markets to enhance transparency and accountability. However, practices may vary across different countries based on their institutional frameworks and regulatory environments.
- The Federal Reserve’s transparency practices have influenced other central banks to adopt similar approaches to communication and decision-making.
- Differences in institutional frameworks and regulatory environments may result in varying levels of transparency and accountability among central banks globally.
- Continued efforts to enhance transparency and accountability remain essential for central banks to maintain public trust and credibility.
