Retirement planning for self-employed sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with American high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset.
As we dive into the world of retirement planning for self-employed individuals, we uncover the importance of financial foresight and strategic decision-making for a secure future.
Importance of Retirement Planning for Self-Employed Individuals
Retirement planning is crucial for self-employed individuals as they do not have access to employer-sponsored retirement plans like 401(k)s or pensions. Without proper planning, self-employed individuals may struggle to maintain their lifestyle during retirement.
Benefits of Starting Retirement Planning Early
- Compound Interest: Starting early allows your investments to grow over time with the power of compound interest.
- Financial Security: Early planning ensures a stable financial future and reduces the risk of running out of money during retirement.
- Flexibility: By starting early, you have more time to adjust your retirement savings strategies as needed.
Risks of Not Having a Solid Retirement Plan
- Financial Insecurity: Without a solid retirement plan, self-employed individuals may face financial insecurity during retirement.
- Lack of Savings: Not having a retirement plan in place can lead to insufficient savings to cover living expenses in retirement.
- Dependency on Others: Without a retirement plan, self-employed individuals may have to rely on others or government assistance for financial support in retirement.
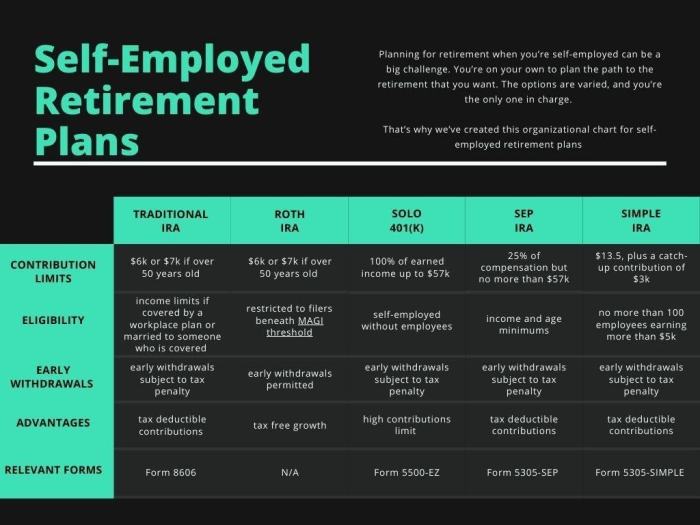
Types of Retirement Accounts for Self-Employed
When it comes to saving for retirement as a self-employed individual, there are several options to choose from. Each type of retirement account has its own set of rules, contribution limits, and tax benefits. It’s important to understand these differences to make an informed decision based on your financial goals and business structure.
SEP-IRA (Simplified Employee Pension Individual Retirement Account)
A SEP-IRA is a retirement account that allows self-employed individuals and small business owners to contribute a percentage of their income, up to a certain limit. One of the key advantages of a SEP-IRA is its high contribution limit, which can be up to 25% of your net earnings from self-employment.
Solo 401(k)
A Solo 401(k) is another popular retirement account option for self-employed individuals. It allows you to contribute both as an employee and as an employer, potentially leading to higher contribution limits compared to a SEP-IRA. Solo 401(k) plans also offer a variety of investment options for your retirement savings.
SIMPLE IRA (Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees Individual Retirement Account)
The SIMPLE IRA is a retirement plan specifically designed for small businesses with fewer than 100 employees. It allows for both employer and employee contributions, making it a flexible option for self-employed individuals. While the contribution limits are lower compared to a Solo 401(k), the administrative requirements are less burdensome.
Strategies for Saving and Investing for Retirement
Saving and investing for retirement is crucial for self-employed individuals to ensure financial security in their golden years. By implementing effective strategies, they can build a nest egg that will support them through retirement.
The Importance of Diversification in Retirement Investment Portfolios
Diversification is key in retirement investment portfolios as it helps spread risk and maximize returns. By investing in a mix of assets such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, self-employed individuals can reduce the impact of market fluctuations on their savings. This approach helps to safeguard their retirement funds and ensures a more stable financial future.
Examples of Investment Vehicles for Self-Employed Individuals
- Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs): IRAs offer tax advantages and a wide range of investment options. Self-employed individuals can choose between a Traditional IRA or a Roth IRA based on their financial goals and tax situation.
- Solo 401(k): A Solo 401(k) allows self-employed individuals to contribute both as an employer and employee, enabling higher contribution limits compared to other retirement accounts. This can help them save more for retirement while reducing their taxable income.
- Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA: A SEP IRA is a tax-deferred retirement plan that allows self-employed individuals to contribute a percentage of their income, making it a flexible option for retirement savings.
- Health Savings Account (HSA): While primarily used for healthcare expenses, an HSA can also serve as a retirement savings vehicle for self-employed individuals. Contributions are tax-deductible, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free, making it a tax-efficient way to save for retirement.
Tax Considerations for Retirement Planning
When it comes to retirement planning for self-employed individuals, understanding the tax implications is crucial. By strategically managing retirement savings, self-employed individuals can minimize their tax liabilities and take advantage of various deductions and credits.
Impact of Retirement Planning on Tax Liabilities
Retirement planning can have a significant impact on tax liabilities for self-employed individuals. Contributions made to retirement accounts such as a Solo 401(k) or SEP IRA are typically tax-deductible, reducing taxable income for the year. This means that the more you save for retirement, the less you may owe in taxes.
Tax Deductions and Credits for Self-Employed Individuals
Self-employed individuals who contribute to retirement accounts may be eligible for tax deductions and credits. For example, contributions to a SEP IRA or Solo 401(k) are tax-deductible, allowing self-employed individuals to lower their taxable income. Additionally, the Saver’s Credit provides a tax credit for eligible individuals who contribute to retirement savings accounts.
Optimizing Retirement Savings to Minimize Tax Burdens
To optimize retirement savings and minimize tax burdens, self-employed individuals can consider maximizing their contributions to retirement accounts. By taking full advantage of tax-deductible contributions, individuals can reduce their taxable income and potentially lower their tax liability. It’s important to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to explore all available options and ensure that retirement planning aligns with tax-saving strategies.
