When it comes to secured vs unsecured loans, buckle up as we take a deep dive into the world of borrowing money. Get ready for a ride filled with valuable insights and crucial information that can help you make informed financial decisions.
In the following paragraphs, we’ll explore the nuances between secured and unsecured loans, shedding light on the advantages, risks, eligibility criteria, and more.
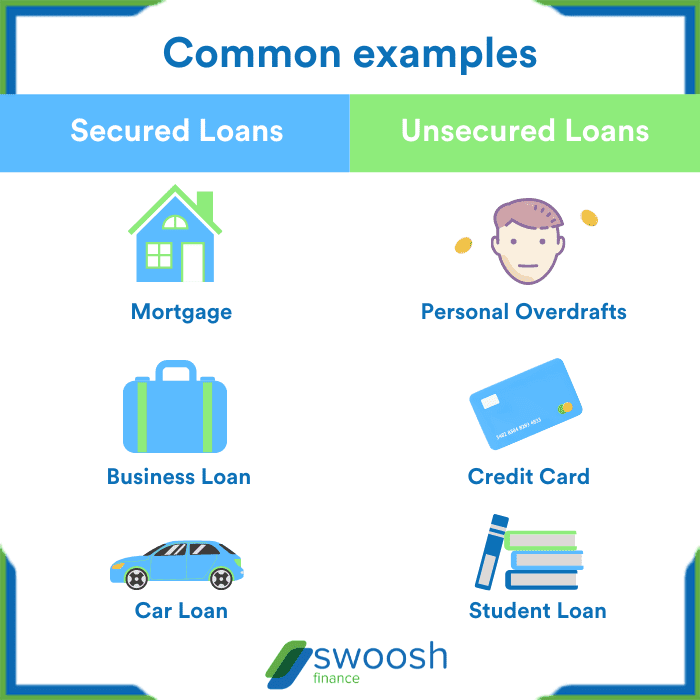
Secured Loans
Secured loans are loans that are backed by collateral, which is an asset that the borrower owns and offers to the lender as a guarantee for the loan. In the event that the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender has the right to seize and sell the collateral to recover the amount owed.
Assets commonly used to secure loans
- Real estate properties (e.g., homes, land)
- Automobiles
- Investment accounts (e.g., stocks, bonds)
- Jewelry or valuable collectibles
Advantages of secured loans
- Lower interest rates compared to unsecured loans due to reduced risk for the lender
- Potential for higher borrowing limits based on the value of the collateral
- Opportunity for borrowers with poor credit to access financing
Potential risks associated with secured loans
- Risk of losing the collateral if unable to repay the loan, leading to financial loss
- Possibility of damaging credit score if defaulting on payments
- May require appraisal and insurance for the collateral, adding to the cost of the loan
Unsecured Loans
Unsecured loans are loans that are not backed by collateral, such as a house or car. These loans are approved based on the borrower’s creditworthiness and ability to repay the loan.
Differences between Secured and Unsecured Loans
Secured loans require collateral, while unsecured loans do not. Secured loans typically have lower interest rates due to the lower risk for the lender, while unsecured loans have higher interest rates. In the case of default, the lender can seize the collateral for secured loans, but for unsecured loans, the lender may have to take legal action to recover the funds.
Examples of Popular Unsecured Loan Types
- Personal Loans: These are general purpose loans that can be used for various personal expenses.
- Credit Cards: Credit cards are a form of unsecured credit that allows users to make purchases up to a certain limit.
- Student Loans: Many student loans are unsecured and are used to cover educational expenses.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Opting for an Unsecured Loan
- Benefits:
- No collateral required: Borrowers don’t have to risk losing their assets.
- Quick approval: Unsecured loans are often approved faster than secured loans.
- Flexibility: Funds from unsecured loans can be used for various purposes.
- Drawbacks:
- Higher interest rates: Unsecured loans typically come with higher interest rates compared to secured loans.
- Stricter eligibility criteria: Borrowers need a good credit score and income to qualify for unsecured loans.
- Lower loan amounts: Due to the higher risk for lenders, unsecured loans may have lower borrowing limits.
Collateral
When it comes to loans, collateral plays a crucial role in determining the terms and conditions of the borrowing agreement. Collateral is an asset or property that the borrower pledges to the lender as security for the loan. In the event that the borrower defaults on the loan, the lender has the right to seize the collateral to recoup their losses.
Types of Collateral
- Real Estate: Properties such as homes, land, or commercial buildings.
- Automobiles: Cars, trucks, motorcycles, or other vehicles.
- Financial Assets: Stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or savings accounts.
- Jewelry: Gold, diamonds, or other valuable pieces.
Impact on Loan Amount and Interest Rates
Collateral significantly affects the loan amount and interest rates offered by lenders. The value of the collateral determines the maximum amount that can be borrowed. Lenders use the collateral to assess the level of risk involved in the loan, with lower-risk loans typically resulting in lower interest rates. In some cases, borrowers may even be able to secure larger loan amounts or better interest rates by offering high-value collateral.
Default and Collateral
In the unfortunate event of default, the lender has the legal right to seize the collateral provided by the borrower. The collateral is then sold to recover the outstanding loan amount. If the sale of the collateral does not cover the full debt, the borrower may still be responsible for the remaining balance. It’s essential for borrowers to understand the risks involved in using collateral to secure a loan and to ensure they can meet the repayment terms to avoid losing their assets.
Eligibility and Approval Process
To secure a loan, it’s crucial to understand the eligibility criteria and approval process for both secured and unsecured loans.
Typical Eligibility Criteria for Secured Loans
- Stable income source
- Adequate collateral (e.g., home, car)
- Good credit score
Contrast in Approval Process
Secured loans are easier to approve as they are backed by collateral, providing security for the lender. Unsecured loans, on the other hand, require a thorough check of credit history and financial stability.
Importance of Credit History in Unsecured Loans
Your credit history plays a significant role in securing unsecured loans. Lenders rely heavily on your credit score to assess your repayment capability and financial responsibility.
Tips for Improving Eligibility
- Make timely payments on existing debts to improve credit score
- Reduce outstanding debt to income ratio
- Maintain a stable employment history
